Delve into the world of ERP analytics to discover how businesses harness data for informed decision-making and operational efficiency. As organizations navigate the complexities of data analysis, ERP analytics emerge as a crucial tool in streamlining processes and driving growth.
Explore the realm of ERP analytics and uncover the transformative power of data-driven insights in shaping business strategies and enhancing performance.
Introduction to ERP Analytics
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) analytics is a process of analyzing data generated within an ERP system to gain insights and improve business operations. It plays a crucial role in helping organizations make informed, data-driven decisions that can lead to increased efficiency and profitability.
Types of Data Analyzed in ERP Systems
ERP systems analyze various types of data to provide a comprehensive view of the organization’s performance and operations. Some of the key types of data analyzed in ERP systems include:
- Financial Data: ERP analytics can analyze financial data such as revenue, expenses, and profitability to help organizations track financial performance and make informed budgeting decisions.
- Inventory Data: By analyzing inventory data, organizations can optimize stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and ensure timely order fulfillment.
- Human Resources Data: ERP analytics can help organizations track employee performance, manage payroll, and optimize workforce planning.
- Sales and Customer Data: Analyzing sales and customer data can provide insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends, helping organizations improve customer satisfaction and target their marketing efforts effectively.
Key Components of ERP Analytics

ERP analytics is a crucial tool for businesses to extract valuable insights from their enterprise resource planning data. It consists of several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive view of the organization’s operations and performance.
Main Components of ERP Analytics
- Data Integration: This component involves collecting data from various sources within the organization and consolidating it into a single, centralized database for analysis.
- Data Warehousing: Data warehousing is the process of storing and managing large volumes of data in a structured format, making it easier to access and analyze.
- Reporting and Dashboards: Reporting tools and dashboards allow users to visualize data in a meaningful way, providing insights into key performance indicators and trends.
- Advanced Analytics: This component includes tools for predictive modeling, data mining, and statistical analysis to uncover patterns and correlations in the data.
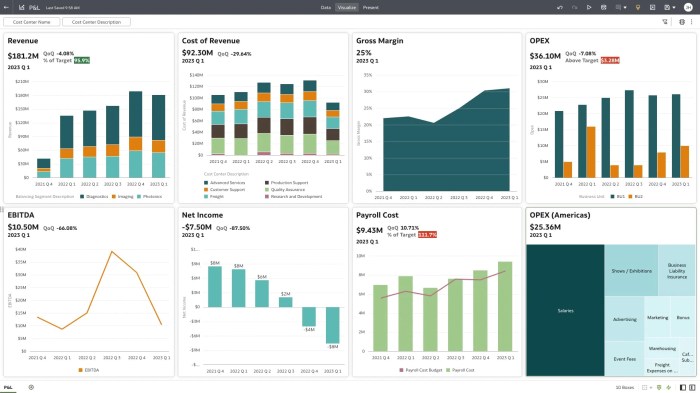
Role of Data Visualization in ERP Analytics
Data visualization plays a crucial role in ERP analytics by transforming complex data sets into interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards that are easy to understand. Visual representations help users identify trends, anomalies, and opportunities for improvement more effectively than raw data alone.
Integration with Other Business Intelligence Tools
ERP analytics can integrate seamlessly with other business intelligence tools such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, supply chain management software, and financial reporting tools. This integration allows organizations to gain a holistic view of their operations and make informed decisions based on comprehensive data analysis.
Implementing ERP Analytics
Implementing ERP analytics in an organization involves several key steps to ensure successful deployment and utilization of analytics tools to drive business insights and decision-making.
Steps Involved in Implementing ERP Analytics
- Assessing organizational readiness and defining objectives: Before implementing ERP analytics, it is crucial to assess the organization’s readiness for analytics adoption and clearly define the objectives and goals to be achieved.
- Choosing the right ERP analytics solution: Selecting the appropriate ERP analytics solution that aligns with the organization’s needs and requirements is essential for successful implementation.
- Data preparation and integration: Ensuring data accuracy, quality, and integration from various sources into the ERP system is a critical step in implementing ERP analytics.
- Training and change management: Providing adequate training to employees on how to use the ERP analytics tools effectively, along with implementing change management strategies to ensure smooth adoption.
- Testing and validation: Conducting thorough testing and validation of the ERP analytics system to identify any issues or discrepancies before full deployment.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement: Establishing processes for continuous monitoring of analytics performance and making improvements based on feedback and insights gained.
Challenges Faced During ERP Analytics Implementation
- Data quality issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can hinder the effectiveness of ERP analytics and lead to incorrect insights.
- Lack of skills and expertise: Organizations may face challenges in finding employees with the necessary skills and expertise to effectively use ERP analytics tools.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist adopting new analytics technologies, requiring effective change management strategies to overcome resistance.
- Integration complexities: Integrating data from multiple sources and systems into the ERP analytics platform can be complex and time-consuming.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Analytics Deployment
- Engage stakeholders: Involving key stakeholders from different departments in the ERP analytics implementation process to ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Start with pilot projects: Conducting pilot projects to test the ERP analytics solution on a smaller scale before full implementation can help identify and address any issues early on.
- Focus on data governance: Establishing strong data governance practices to ensure data quality, security, and compliance throughout the ERP analytics implementation.
- Provide ongoing training and support: Offering continuous training and support to employees to enhance their skills and capabilities in using ERP analytics tools effectively.
- Monitor performance and ROI: Regularly monitoring the performance of ERP analytics tools and measuring the return on investment to evaluate the success of the deployment.
Benefits of ERP Analytics
Using ERP analytics offers a range of advantages for businesses looking to optimize their operations and decision-making processes. By leveraging data-driven insights, companies can drive improvements in various aspects of their organization, leading to increased efficiency and profitability.
Enhanced Decision-Making
ERP analytics provide real-time access to critical data and key performance indicators, enabling decision-makers to make informed and strategic decisions. By having a comprehensive view of their operations, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and opportunities that may not be apparent through traditional reporting methods.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Through the use of ERP analytics, organizations can streamline processes, identify bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation. By analyzing data on various operational aspects, such as production, inventory, and supply chain management, businesses can drive efficiencies and cost savings.
Increased Visibility and Transparency
ERP analytics offer a centralized platform for data analysis, providing stakeholders with a clear and comprehensive view of the organization’s performance. This increased visibility enhances transparency within the company, enabling better collaboration and alignment across departments.
Enhanced Forecasting and Planning
By leveraging predictive analytics capabilities, ERP systems can help businesses forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and plan resources more effectively. This proactive approach to forecasting and planning allows companies to better anticipate market trends and capitalize on opportunities.
Cost Savings and Revenue Growth
By optimizing processes, reducing waste, and improving decision-making, ERP analytics can lead to cost savings and increased revenue generation. Through better resource allocation and strategic investments, businesses can drive growth and profitability in a competitive market.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, ERP analytics offer a strategic advantage by enabling businesses to leverage data effectively, optimize operations, and stay ahead of the competition. With a focus on innovation and efficiency, ERP analytics pave the way for sustainable growth and success in today’s dynamic business landscape.
FAQ Insights
What is ERP analytics?
ERP analytics involve the analysis of data within an ERP system to extract valuable insights for decision-making and operational improvements.
How do ERP analytics benefit organizations?
ERP analytics help organizations make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and drive strategic growth through data-driven insights.
What are some common challenges during ERP analytics implementation?
Challenges during ERP analytics implementation may include data integration issues, resistance to change, and ensuring data accuracy.
How does ERP analytics differ from traditional reporting methods?
ERP analytics offer real-time insights, predictive analytics, and a holistic view of business operations compared to static reports provided by traditional methods.
What role does data visualization play in ERP analytics?
Data visualization in ERP analytics helps users interpret complex data sets, identify trends, and communicate insights effectively for informed decision-making.