In the dynamic landscape of modern business, the integration of Business ERP systems has become a crucial element for success. From streamlining operations to enhancing decision-making processes, Business ERP offers a myriad of benefits that propel organizations towards efficiency and growth.
Let’s delve into the world of Business ERP and uncover the key components, benefits, and implementation strategies that drive businesses forward.
Definition of Business ERP
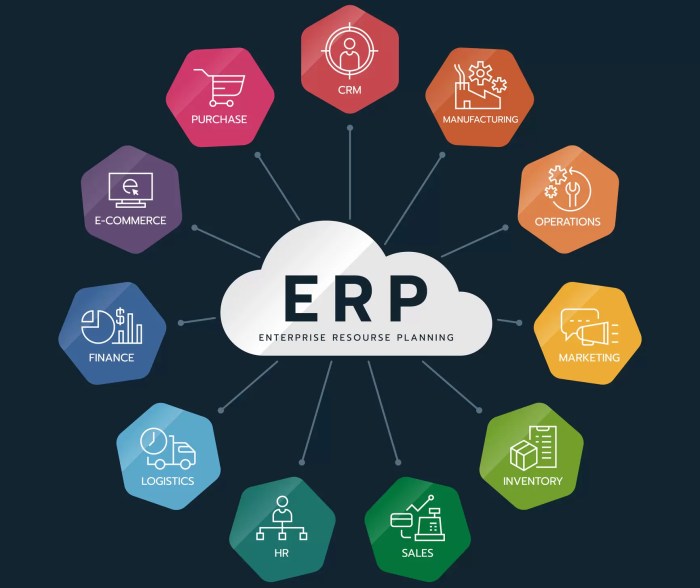
Business ERP, which stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, is a comprehensive software system that integrates and automates core business processes such as accounting, human resources, inventory management, supply chain, and customer relationship management. It helps organizations streamline operations, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Main Features and Functions
- Centralized Database Management: Business ERP systems store all data in a centralized database, ensuring consistency and accuracy across departments.
- Process Automation: Automates repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors and improving productivity.
- Real-time Reporting: Provides up-to-date information for better decision-making.
- Integration Capabilities: Allows seamless integration with other systems for a holistic view of the business.
- Scalability: Adaptable to the growth of the organization, accommodating increased data and user requirements.
Commonly Used in Industries
Business ERP systems are commonly used in industries such as:
- Manufacturing: Helps manage production processes, inventory, and supply chain efficiently.
- Retail: Facilitates inventory management, sales tracking, and customer relationship management.
- Finance: Assists in financial planning, budgeting, and forecasting.
- Healthcare: Streamlines patient data management, billing, and compliance with regulations.
Benefits of Implementing Business ERP
Implementing a Business ERP system can bring a multitude of benefits to an organization. From streamlining processes to improving decision-making, the advantages are numerous.
Enhanced Efficiency
- Business ERP systems automate repetitive tasks, saving time and reducing errors.
- Centralized data storage allows for easy access to information across departments, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
- Improved communication and collaboration among team members result in faster response times and increased productivity.
Increased Productivity
- Integration of various business functions into a single system eliminates silos and improves overall efficiency.
- Real-time data insights enable better resource allocation and more informed decision-making.
- Automated reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into performance metrics, enabling proactive adjustments to strategies.
Enhanced Decision-Making Processes
- Access to real-time data allows for quick and informed decision-making at all levels of the organization.
- Forecasting capabilities help in predicting market trends and adjusting strategies accordingly.
- Customizable dashboards and reports provide a comprehensive view of the business, facilitating strategic planning and goal setting.
Real-World Examples
- Company A, a multinational corporation, saw a 20% increase in productivity after implementing a Business ERP system, leading to significant cost savings.
- Company B, a medium-sized enterprise, experienced a 30% reduction in inventory costs due to improved inventory management and forecasting capabilities provided by a Business ERP solution.
- Company C, a start-up, streamlined its operations and achieved rapid growth by leveraging the scalability and flexibility of a Business ERP system.
Key Components of a Business ERP System
When it comes to a Business ERP system, there are several key components that work together to streamline business processes and improve efficiency.
Essential Modules of a Business ERP System
- Finance and Accounting: This module handles all financial transactions, budgeting, and financial reporting within the organization.
- Human Resources: Manages employee information, payroll, benefits, and performance evaluations.
- Inventory Management: Keeps track of stock levels, orders, and supply chain management.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Helps in managing customer interactions, sales, and marketing efforts.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizes the flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
Integration of Components in a Business ERP System
These components work together seamlessly by sharing data and information across departments. For example, when a sales order is placed, the inventory management module is automatically updated to reflect the change in stock levels. This integration reduces manual data entry and ensures accuracy in information.
Customization Options for Business ERP Systems
- Module Selection: Businesses can choose which modules are most relevant to their operations and customize the ERP system accordingly.
- Workflow Configuration: Tailoring workflows to match specific business processes can enhance efficiency and productivity.
- Reporting Tools: Customizing reports and dashboards allows businesses to track key performance indicators and make informed decisions.
Implementation of Business ERP
Implementing a Business ERP system is a crucial process that requires careful planning and execution to ensure success. From initial setup to employee training, each step plays a vital role in the overall implementation process.
Steps for Successful Implementation
- Planning: Define clear objectives, allocate resources, and establish a timeline for the implementation process.
- Selection: Choose the right ERP system that aligns with your business needs and goals.
- Customization: Tailor the ERP system to meet your specific requirements through configuration and integration.
- Data Migration: Transfer existing data into the new ERP system without compromising data integrity.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any issues before full deployment.
- Training: Provide comprehensive training to employees to ensure they can effectively use the new ERP system.
- Go-Live: Roll out the ERP system to all users and monitor its performance to address any post-implementation issues.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Lack of Top Management Support: Ensure top management is actively involved and supports the ERP implementation to drive the process forward.
- Resistance to Change: Communicate the benefits of the ERP system to employees and involve them in the implementation process to overcome resistance.
- Data Integration Issues: Address data integration challenges by conducting thorough data mapping and testing to ensure seamless integration.
- Insufficient Training: Provide ongoing training and support to employees to help them adapt to the new ERP system and maximize its benefits.
Tips for Employee Training
- Provide Hands-On Training: Offer practical training sessions that allow employees to interact with the ERP system and learn by doing.
- Offer Continuous Support: Establish a support system to address any questions or issues that arise during the training process and beyond.
- Create Training Materials: Develop comprehensive training materials, including manuals, videos, and FAQs, to assist employees in using the ERP system effectively.
Ultimate Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of Business ERP, it’s evident that the strategic integration of this system can revolutionize how businesses operate. By embracing the power of Business ERP, organizations can unlock new levels of efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in today’s fast-paced market environment.
The journey to success begins with embracing innovation and leveraging the transformative capabilities of Business ERP.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of Business ERP?
Business ERP plays a vital role in modern business operations by integrating various functions into a unified system, enhancing efficiency and decision-making.
How can Business ERP benefit organizations?
Implementing Business ERP can lead to improved efficiency, productivity, and streamlined processes, ultimately boosting organizational performance.
What are some common challenges during Business ERP implementation?
Organizations often face challenges such as data migration, resistance to change, and ensuring effective employee training during the implementation phase of Business ERP.